The right action at the right time – advanced response capabilities in EDR

Endpoint Detection and Response is a crucial part of defending your company against attack. Here, we shine a light on the ‘response’ aspect, given it can make the difference between being able to sweep up a minor attack quickly and having to deal with a full-scale data breach.
Response – as the name suggests – is essentially how quickly you can react to an attack. Being able to react quickly to a cyber incident and mitigate the risk once it has been identified reduces the amount of time an attacker can operate in your infrastructure. This, in turn, limits the damage that is done.
Detection capabilities are now highly automated, but for a long time the response has been a more manual endeavor. Having spoken to our customers and partners, it has become very clear that there is a real need to automate various response actions, as well as simultaneously executing other actions across multiple endpoints to boost productivity. When you are able to accurately detect threats and understand the threat landscape, it becomes easier to align your response and with minimum disruption.
Further, there is also a need for different types of responses depending on the situation at hand. Essentially, when you can accurately detect threats and understand what is happening, you’re able to align your response with minimal disruption.
The result of this dialogue is that we have been able to add many new response actions to the Microsoft Windows version of our Elements Endpoint Detection and Response product. These can be remotely triggered for one or multiple endpoints at the same time and are available globally.
Acting, not just knowing
So, let’s dig a little deeper into response and what it means for you in reality. This capability allows you to enrich forensic artefacts from endpoints and therefore fight back against attackers. It also puts you in the driving seat by giving you the ability to slow down or even completely stop an attacker from achieving their objective – for example, by degrading command and control actions. You can also rapidly contain threats as they are discovered and stop attackers from getting any further in real time.
We have divided response capability into three parts:
- Investigative actions
- Containing actions
- Remediating actions
Investigative actions
- Collect Forensics Package
- Enumerate Process
- Enumerate Scheduled Task
- Enumerate Services
- Full Memory Dump
- Map File System
- Map Registry
- Netstat
- Retrieve Anti-Virus Log Files
- Retrieve Event Log Files
- Retrieve Files
- Retrieve Folders
- Retrieve Master Boot Record
- Retrieve Master File Table
- Retrieve PowerShell history
- Retrieve Process Memory Dump
- Retrieve Registry Hives

And there’s more.
The event search tool can be used to search data already sent to the EDR Backend related to Broad Context Detection.
In case the attack is too complex to comprehend, WithSecure’s elite threat hunting team is at your service 24/7, ready to find a solution.
Please note:
Retrieving data can be done for multiple endpoints with a single action to increase productivity.
Additionally, in case the endpoint is not online when the request for additional information is made, the endpoint agent will immediately deliver the information as soon as it is back online.
Containment actions
- Control Applications
- Kill Process
- Kill Thread
- Network Isolation
After the investigation phase, your IT admin or WithSecure Partner managing the detection and response service can contain the attack and stop them in their tracks.
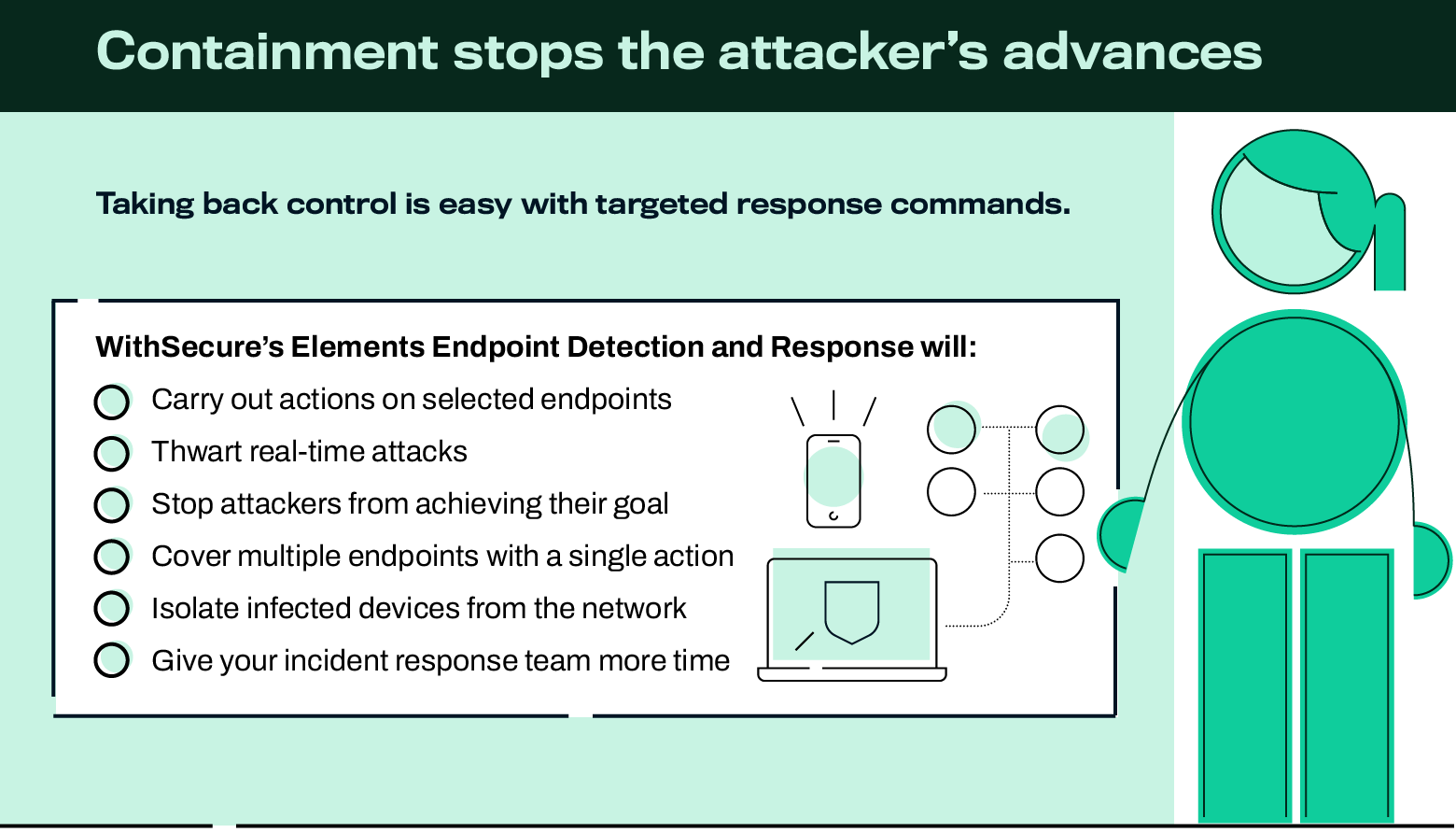
Furthermore, it will kill process containment actions, ensuring specified processes are terminated remotely on specific endpoints
Elements Endpoint Protection’s Application Control functionality can be used in cases where there is a known malicious program on a target endpoint and you want to prevent it from being run again.
Application control is part of Elements Endpoint Protection’s device profile, so the rule is typically applied to larger groups of endpoints at once, as it’s linked to device profiles.
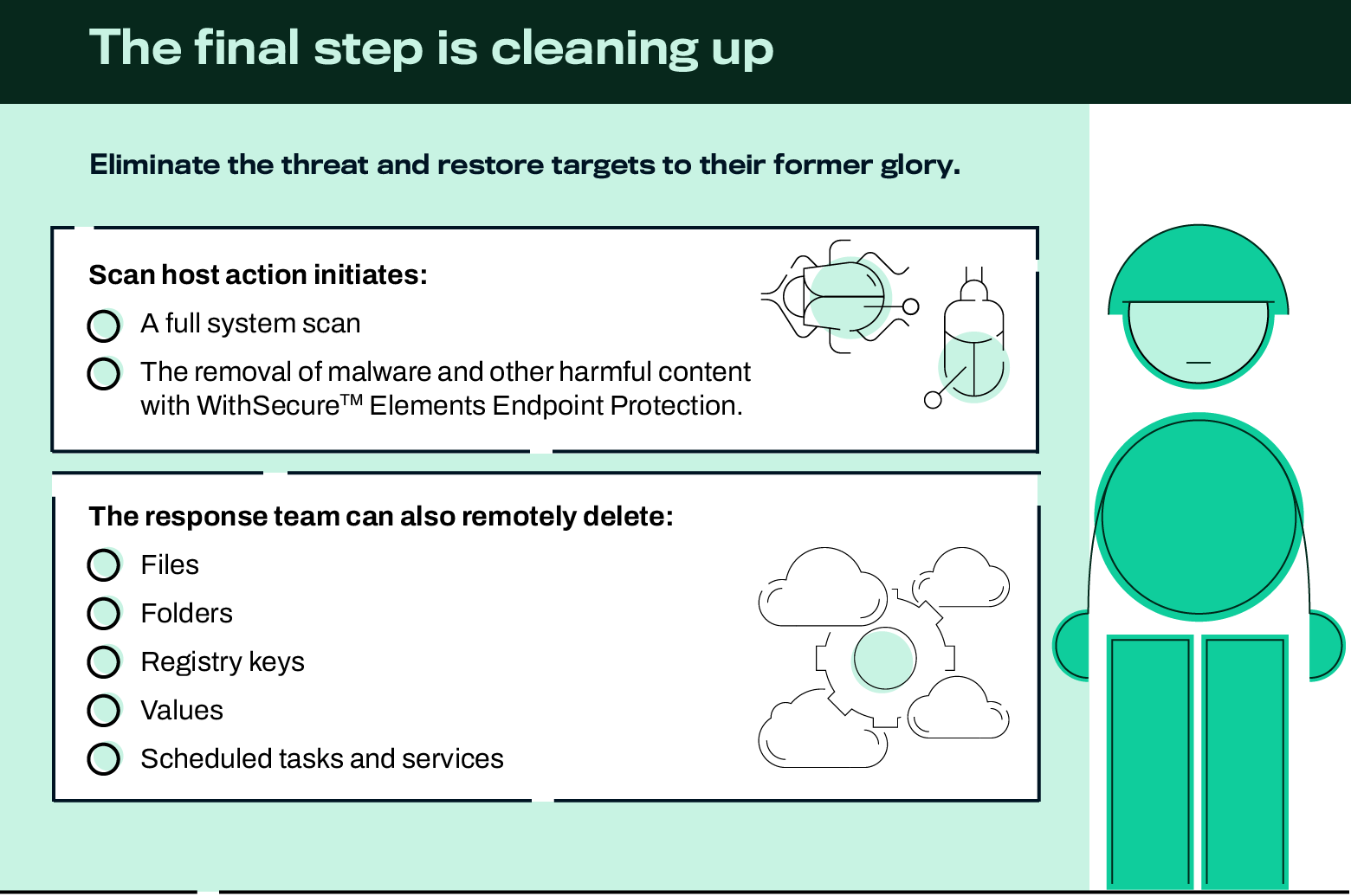
Remediation actions
- Delete File
- Delete Folder
- Delete Registry Key
- Delete Registry Value
- Delete Scheduled Task
- Delete Service
- Inform users
- Scan host
The final layer of protection ensures that the attacker does not achieve persistency on an already compromised system.
Finally, Inform Users can be used to compose and send an alert email to users of the affected hosts.